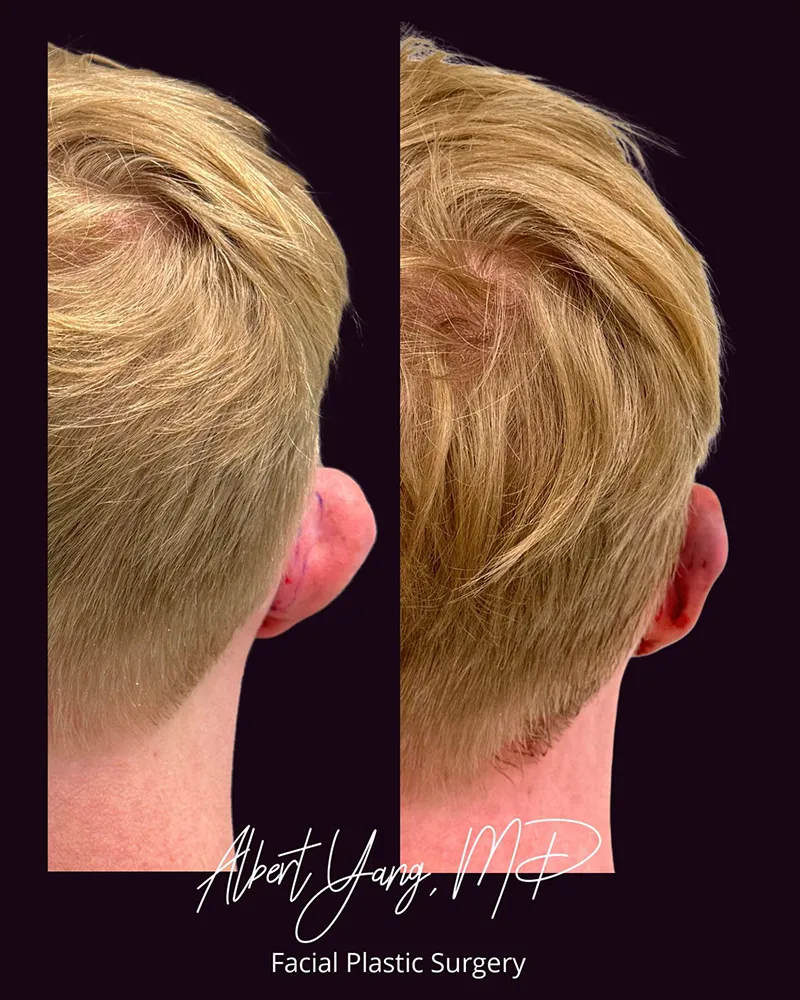
Otoplasty
Conveniently located to serve Seattle and Bellevue
Jump To
Otoplasty Ear Pinning
What is an otoplasty?
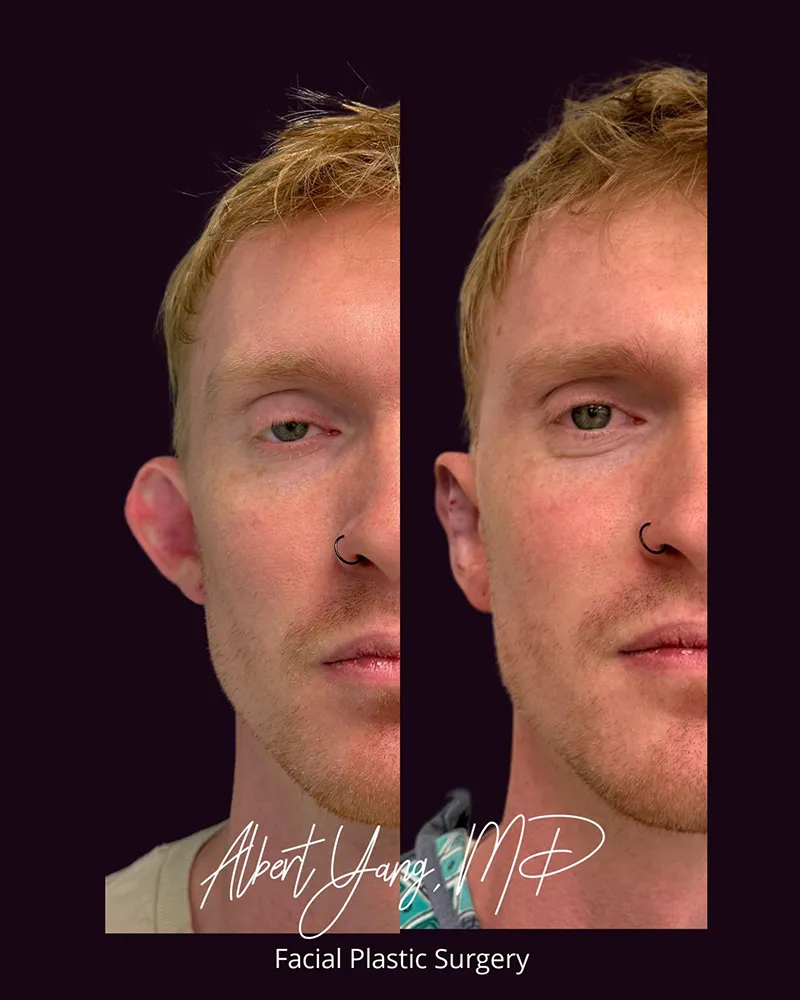
Otoplasty is a type of cosmetic ear surgery that reshapes, repositions, or adjusts the size of the ears. The goal is to create ears that look natural and proportionate to the face. Most commonly, otoplasty is performed to correct prominent ears (ears that stick out too far from the head). It can also address other ear differences, such as congenital deformities (e.g., anotia, microtia) or earlobe defects.
Who is a candidate?
Otoplasty is an elective procedure for healthy individuals who are concerned about the appearance of their ears.
- Children: Surgery is usually done after the ears have mostly finished growing, around ages 5–6. Early correction can help reduce the risk of bullying or teasing at school.
- Adults: Surgery can improve self-esteem and confidence by creating a more balanced ear appearance.
What does the surgery involve?
Otoplasty is generally well-tolerated by both children and adults.
- Incisions: Hidden behind the ear to minimize visible scarring.
- Techniques:
- The most common cause of prominent ears is an underdeveloped antihelical fold, which can be recreated with sutures to bring the ear closer to the head.
- An enlarged conchal bowl can be reduced or repositioned to improve ear projection.
- The specific approach depends on the individual’s ear anatomy.
Recovery
- After surgery, the ears are protected with a head wrap. Mild discomfort and a feeling of tightness are normal.
- The head wrap is usually removed after a few days and replaced with a light headband to prevent accidental bending of the ears.
- Sutures are either dissolvable or removed within about a week.
- Bruising may last 2–4 weeks.
- Swelling typically improves by 6 weeks.
- Final results are usually visible around 3 months after surgery.
Complications
Complications are uncommon but can occur:
- Early concerns: Bleeding (disproportionate pain or swelling) or infection.
- Late concerns: Minor asymmetry or slight recurrence of ear projection. Scarring and keloid is uncommon.
- Most issues are mild and can be addressed if necessary. Always discuss any concerns with your surgeon.