Chemical Peels
Conveniently located to serve Seattle and Bellevue
Jump To
What is a chemical peel?
A chemical peel is a time honored treatment for skin rejuvenation, with roots tracing back to ancient Egypt and Rome. Historical records suggest that Cleopatra famously bathed in sour milk, rich in lactic acid, to enhance her complexion.
Modern chemical peels work on a similar principle. They create controlled damage to the skin, triggering the body’s natural healing response. This process stimulates skin regeneration and soft tissue remodeling by increasing collagen production. The result is improved skin tone, texture, pigmentation, and a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles.
Chemical peels are commonly performed on the face, neck, and hands, and are used for both medical purposes such as removing sun damaged or pre-cancerous skin cells and for aesthetic enhancement.
Conditions that benefit from Chemical Peels:
- Acne scarring
- Sun Damage (eg. Actinic keratoses)
- Wrinkles
- Uneven skin tone (eg. xanthelasma, melasma, solar lentigines or sun spots)
- Rough or dull skin texture
- Lip rejuvenation
Type of Chemical peels
Chemical peels help improve skin tone, texture, pigmentation, and fine lines. The effectiveness of the treatment depends on how deeply the peel penetrates into the skin layers.
| Types of Peels | Depth | Recovery Time | Examples | Best for | Sedation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superficial | Epidermis | 1-3 days |
|
Dark spot, skin tone | Awake |
| Medium | Papillary Dermis | 5-7 days |
|
Dark spot, tone, light wrinkles, acne scars | Anxiolytic (eg. Xanax) |
| Deep | Mid-Reticular Dermis | 2+ weeks |
|
Severe wrinkles | Light sedation with heart monitor |
Medical conditions that may affect chemical peel
- Allergy to ingredients in chemical in peel
- Pregnant woman or breast feeding
- Patient on birth control (Due to estrogen level)
- Significant sun exposure
- Darker skin types
- History of keloid or hypertrophic scar
- History of radiation
- Active skin infection
- Isotretinoin (stop 12-24 months prior to peel)
- Chronic smokers
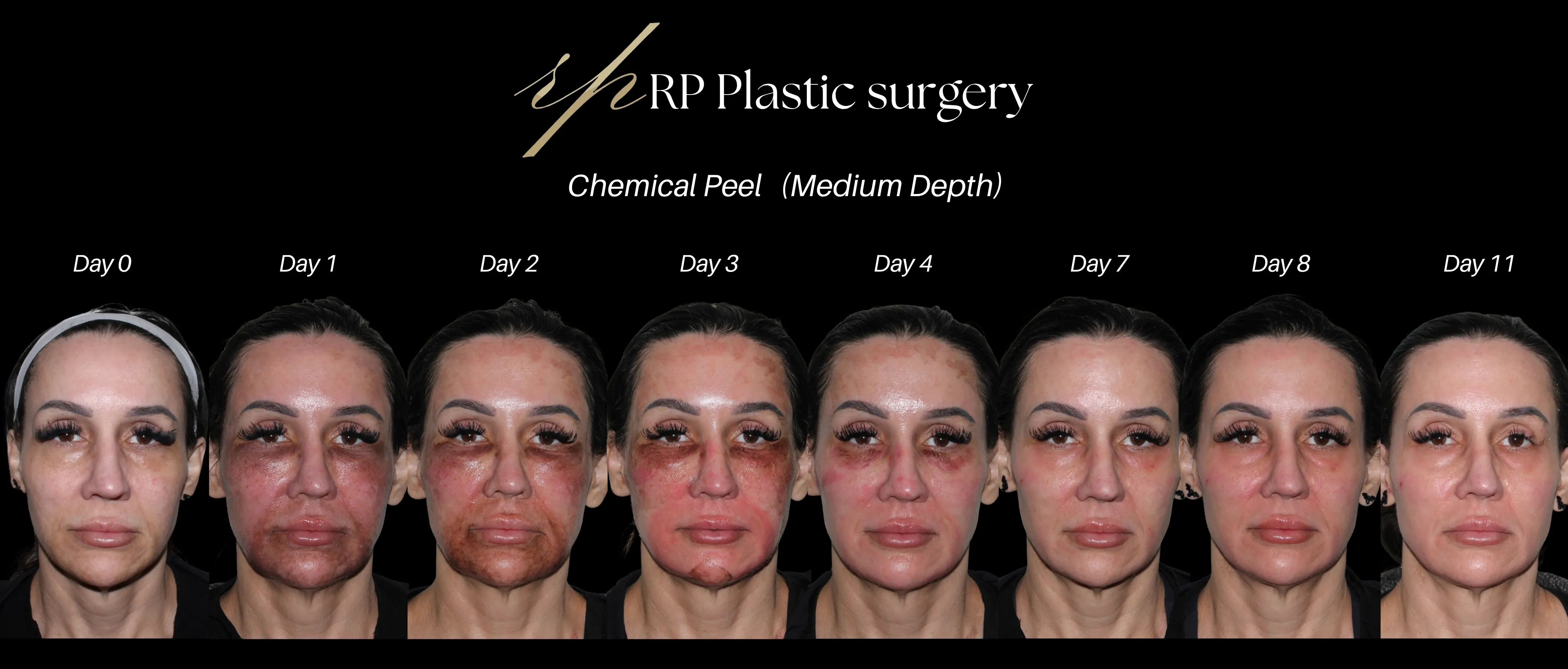
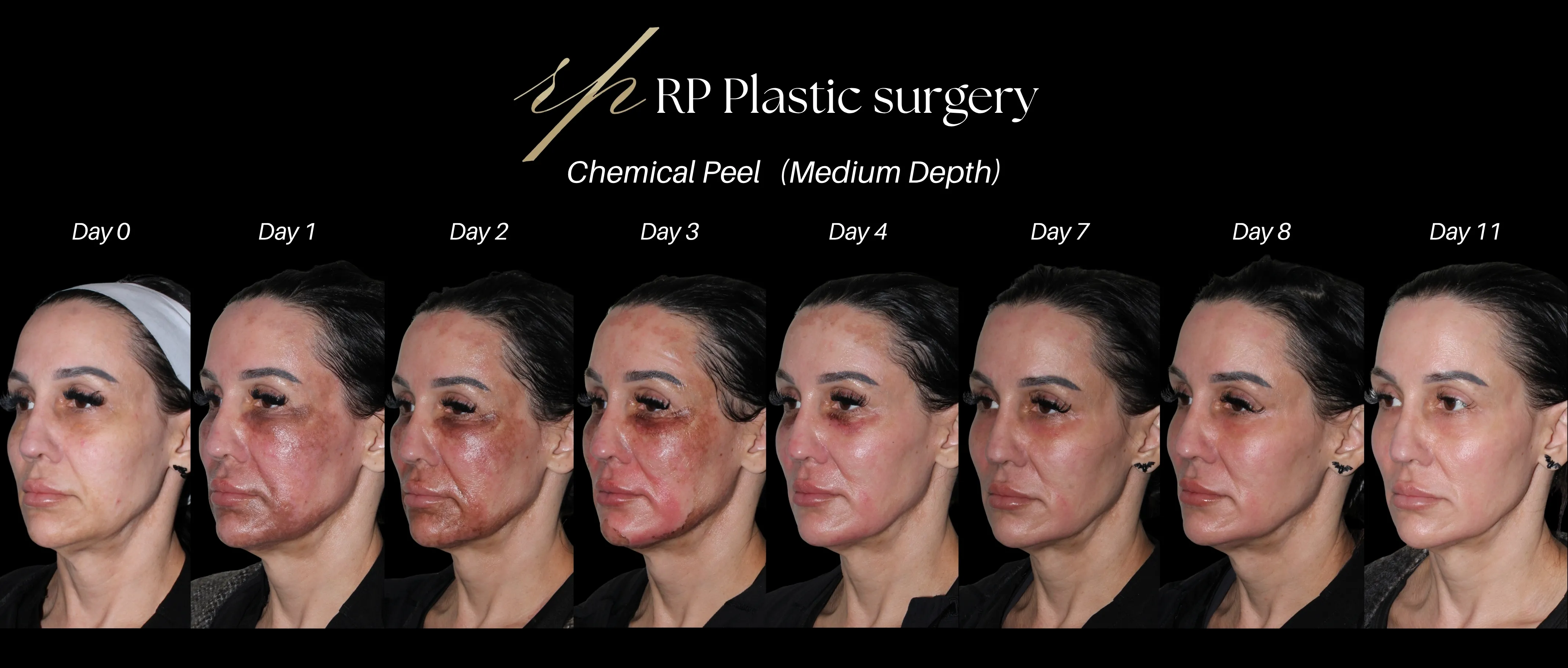
What are the before/after care like?
Note: Care instructions may vary depending on the type of peel and your provider’s specific recommendations. Always follow your clinician’s guidance closely.
🧴 3–4 Weeks Before the Peel (Pretreatment Phase)
- Begin using brightening agents such as hydroquinone and rejuvenating products like tretinoin if recommended by your provider.
- These help prepare your skin, even out pigmentation, and enhance the peel’s results.
- Avoid sun exposure and always use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+).
🚫 2 Days Before the Peel
- Stop all active skincare products (e.g., retinoids, hydroquinone, exfoliants).
- Start any prescribed antibiotics or antiviral medications to prevent infection or herpes simplex reactivation.
- Avoid waxing, shaving, or using harsh cleansers.
💆♀️ Day of the Peel
- Come to your appointment with a clean face – no makeup, lotion, or perfume on the treatment area.
- After the peel, keep your skin moist using an emollient such as Aquaphor.
- Apply sunscreen daily and avoid direct sunlight
🌤 Days 1–7 After the Peel
- Continue using your moisturizer and sunscreen.
- You may notice some peeling or flaking — this is normal.
- Do not pick or peel the skin.
- If necessary, you may trim loose skin gently with clean scissors
- Continue antibiotics/antivirals as directed (usually stop after 5–7 days).
🌸 After 7 Days
- The skin should be mostly healed.
- You can gradually restart your skincare products, such as brightening or anti-aging creams.
- Continue sun protection daily to maintain results.
- Broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+)
What are possible side effects?
Chemical peels are generally safe when performed by trained professionals. However, as with any medical or cosmetic procedure, there are potential risks and side effects, especially with deeper peels or when aftercare instructions aren’t followed properly.
- Prolong redness
- Skin blister / prolonged healing
- Infection
- Temporary or permanent pigment change of the skin
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): Refers to areas of skin that become darker after a chemical peel. This is more common in patients with darker skin tones or in those who have excessive sun or heat exposure. Pretreatment and post treatment of the skin is important to minimize the risk of PIH.
- Scarring
- Allergic reaction
- Heart or kidney toxicity (in deep phenol peels)
